JAVA多线程手记——多线程初探
问题描述
编写一个有两个线程的程序,第一个线程用来计算1~100之间的偶数及个数,
第二个线程用来计算1-100之间的偶数及个数。
知识回顾:多线程两种基本实现方式
1. 继承Thread类
2. 实现Runnable接口
1.继承Thread类
//Thread类结构:
public class Thread implements Runnable
//继承Thread类
public class MyThread extends Thread{
@override
public void run(){
super.run();
System.out.println("MyThread");
}
}
2.实现Runnable接口
public class MyRunnable implements Runnable{
@override
public void run(){
System.out.println("running!");
}
}
3.第一次尝试解决问题
public class Even extends Thread {
private int count;//记录奇数数目
@Override
//采取多线程的第一种实现方式
public void run() {
super.run();//调用Thread类的run()
for (int i = 2; i < 100; i += 2) {
System.out.print(i+" ");
count++;
}
System.out.println("\nThe number of even number is "+count);
}
--------------------------------------------------------------
public class Odd extends Thread {
private int count;//记录奇数数目
@Override
//采取多线程的第一种实现方式
public void run() {
super.run();//调用Thread类的run()
for (int i = 1; i < 100; i += 2) {
System.out.print(i+" ");
count++;
}
System.out.println("\nThe number of odd number is "+count);
}
----------------------------------------------------
public class Test{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Even even = new Even();
Odd odd = new Odd();
even.start();
odd.start();
}
}
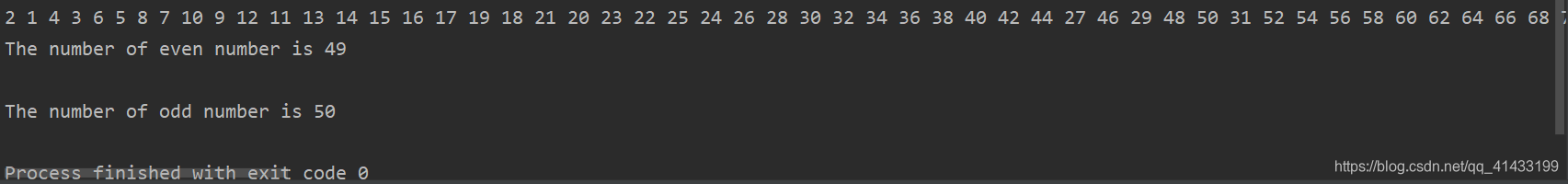
2 1 4 3 6 5 8 7 10 9 12 11 13 14 15 16 17 19 18 21 20 23 22 25 24 26 28 30 32 34 36 38 40 42 44 27 46 29 48 50 31 52 54 56 58 60 62 64 66 68 70 72 74 76 78 80 82 84 33 86 88 90 35 92 37 39 94 41 96 43 98 45 47 49 51 53 55 57 59 61 63 65 67 69 71 73 75 77 79 81 83 85 87 89 91 93 95 97 99
The number of even number is 49
The number of odd number is 50
Process finished with exit code 0
思考:程序交替运行,没有先输出奇数部分,再输出偶数部分,再尝试调整看看
4.改进后,引入Thread.sleep()
//新建MyThread类
public class MyThread extends Thread {
private String type;
private int count;
public MyThread(String name, String type){
super(name);
this.type = type;
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(this.getName() + "运行中......");
if(type.substring(0,1).equals("奇")){
System.out.println("0到100间的奇数如下:");
for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i += 2) {
System.out.print(i+" ");
count++;
}
System.out.println("\n数目为: "+count);
}
try {
sleep(1000);//sleep()使得当前线程进入阻塞状态,系统便开始进行下一次调度,循环往复
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if(type.substring(0,1).equals("偶")){
System.out.println("0到100间的偶数如下:");
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i += 2) {
System.out.print(i+" ");
count++;
}
System.out.println("\n数目为: "+count);
}
}
}
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThread myThread1 = new MyThread("奇数线程","奇数");
MyThread myThread2 = new MyThread("偶数线程","偶数");
Thread Odd = new Thread(myThread1);
Thread Even = new Thread(myThread2);
Odd.start();//猜想:每一次执行run()奇数部分正常执行,然后进入休眠,休眠时间结束后轮到偶数进程执行
Even.start();//相当于每一次偶数进程执行前都要多等待一个休眠,周而复始,导致程序结果是奇数部分整体
//先于偶数部分执行
}
【运行结果】
偶数线程运行中......
奇数线程运行中......
0到100间的奇数如下:
1 3 5 7 9 11 13 15 17 19 21 23 25 27 29 31 33 35 37 39 41 43 45 47 49 51 53 55 57 59 61 63 65 67 69 71 73 75 77 79 81 83 85 87 89 91 93 95 97 99
数目为: 50
0到100间的偶数如下:
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 32 34 36 38 40 42 44 46 48 50 52 54 56 58 60 62 64 66 68 70 72 74 76 78 80 82 84 86 88 90 92 94 96 98
数目为: 50
5.Thread.sleep()
1.sleep():暂停当前线程,把cpu片段让出给其他线程,减缓当前线程的执行
2. 线程睡眠到期自动苏醒,并返回到可运行状态(就绪),不是运行状态。
3、sleep()只能控制当前正在运行的线程,sleep是静态方法,示例中类对象对其进行了调用(因为类对象可以调用类的静态方法)
方法原型:在这里插入代码片
public static native void sleep(long millis) throws InterruptedException;
6.第一次写博客,希望和大家一起交流学习,发现问题也请指正。溜了溜了。。。
转载:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41433199/article/details/102557530
查看评论
